Newsletter
IME Aktuell 49
Topics of this edition:
- GLBO commissioning
- BMBF project ‘ProMotion’ with Gebr. Lödige GmbH
- Block Casting Forum 2025
Aktivitäten & Veranstaltungen
Terminart:
Beschreibung:
Datum:
Die Welt der “Green Metallurgy®”
Das IME Metallurgische Prozesstechnik und Metallrecycling (Professor Dr.-Ing. Dr. h.c. Bernd Friedrich) beschäftigt sich mit angewandter Forschung und Lehre in den Bereichen der extraktiven Metallurgie (Pyrometallurgie und Hydrometallurgie), der Metallveredelung und Elektrolyse sowie dem Recycling von Metallen aus diversen Abfallströmen. Am IME-RWTH werden Prozesse mit optimiertem Ressourceneinsatz und unter Berücksichtigung kritischer Abfallströme (Kreislaufwirtschaft / Circular Economy) entworfen und weiterentwickelt. Weitere wichtige Forschungsgebiete sind die Vakuummetallurgie im Klein- bis hin zum Demo-Maßstab sowie die Synthese von Nanopulver.

| Jahr | Publikationen |
|---|---|
| 2025 |
Beitrag in Fachzeitschrift
Resources, Conservation & Recycling 227 (2026) 108766
Ayesha Tasawar, Daniel Munchen, Alexander Birich, Rungsima Yeetsorn, Walter Sebastian Scheld, Waritnan Wanchan, Benjamin Butz, Bernd Friedrich
|
| 2025 |
Beitrag in Fachzeitschrift
Minerals 2026, 16, 47 https://doi.org/10.3390/min16010047
Soner Top, Mahmut Altiner, Huseyin Vapur, Sait Kursunoglu, Srecko Stopic
|
| 2026 |
Beitrag in Fachzeitschrift
Processes 2026, 14, 33 https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010033
|
Elektronikschrott Recycling
Das IME hat sich zum Ziel gesetzt, das hohe Potential von Elektro- und Elektronik-schrott als Rohstoffressource zu nutzen und einen nachhaltigen, metallurgischen Recyclingprozess für Elektronikschrott zu entwickeln. Im Fokus steht dabei die Wiedergewinnung von Basismetallen (Kupfer, Aluminium), Edelmetallen (Gold, Silber, Platin und Palladium) sowie kritischen Metallen (Gallium, Germanium und Indium). Bei der Ausarbeitung von geeigneten Recyclingkonzepten kann das Institut auf langjährige Erfahrung in der Prozessentwicklung und Optimierung komplexer Stoffsysteme zurückgreifen. Aktuell werden in fünf Promotionsprojekten verschiedene Ansätze pyro- und hydro-metallurgischer Verfahren entwickelt, erprobt und hinsichtlich ihrer Selektivität, Effizienz und Flexibilität analysiert. Die Verfahren zielen auf die Verarbeitung unterschiedlicher Stoffströme (z.B. Leiterplatten, Schredder-Staub, ganze Smartphones) mit dem Ziel, die eingebundenen Wertmetalle verlustfrei zurückzugewinnen.
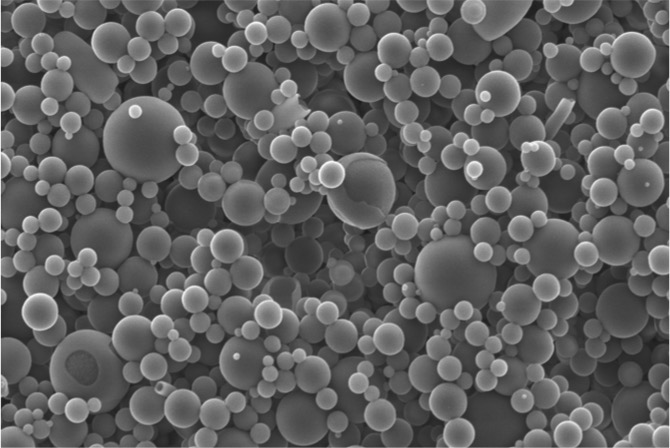
Nanopulver Synthese
Nanotechnology belongs to the key innovative technologies for powder production. Ultrasonic spray pyrolysis USP is a versatile method for the formation of nanosized particles of metals, oxides and composites. Our work deals with nanoparticles of Ag, Cu and Au formed by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis using the horizontal and vertical reactor. Furthermore, a direct synthesis of Ru-TiO2 and RuO2-TiO2 nanoparticles with the core and shell structure was investigated. Molar fractions of precursors, solvent type, and the process temperature play the crucial roles in the formation of core and shell structures.

Kreislaufwirtschaft von Batterien
The IME represents the field of process metallurgy and metal recycling at RWTH Aachen University. Due to the growing public, political and industrial interest in battery recycling the IME has systematically developed optimal pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical recycling concepts for all standard battery systems in cooperation with industrial partners and also in terms of projects funded by the government. Some of these methods have already been implemented industrially and has been rated as BAT (Best Available Technology).
Titan Metallurgie
Titanium is called the material of the future. This title results from the unique combination of properties such as good corrosion resistance, high strength and biocompatibility with low density. Due to these properties, titanium alloys are increasingly being used in areas such as aerospace, automotive, chemical or medical technology. Despite its relative commonness as the fourth most abundant element in the earth’s crust, titanium remains denied a wide industrial use. The reason for this is the high price of the metal, which results from the production costs. To reduce these and thus to allow the titanium the broad mass accessibility is a big challenge in research.

Technologie Metalle (Gewinnung und Recycling)
Critical metals are, by definition, metals that are of high economic importance and at the same time exhibit significant supply risks. Elements that are ascribed as especially critical are, for example, rare earth elements, platinum group metals, but also antimony and niobium. At IME, pyrometallurgical as well as hydrometallurgical processes for economic, efficient and environmentally friendly treatment and extraction of critical metals are investigated. The following list abstracts some of our current research topics in this field:

Aluminiumrecycling und Schmelzreinigung
The working group focuses on the recycling of aluminium scraps via under salt or salt-free processes. Top Blown Rotary Converter (TBRC) in lab and demo-scale is used to perform the experiments. Efficient coagulation during recycling is also studied by using different salt compositions. In addition, thermal treatment of organic containing materials is being investigated to find an optimum process which is a combination of pre-treatment and recycling. Moreover, the working group performs investigations about the melt cleanliness by using different removal and detection technologies to meet the high requirements of the product and material properties. Fundamental researches on particle behaviour in melts such as settling and agglomeration are also on-going to gain more knowledge about particles. Improvement of existing technologies and understanding of the mechanisms are main targets of the activities.

Behandlung von Rückständen und Primärmetallurgie
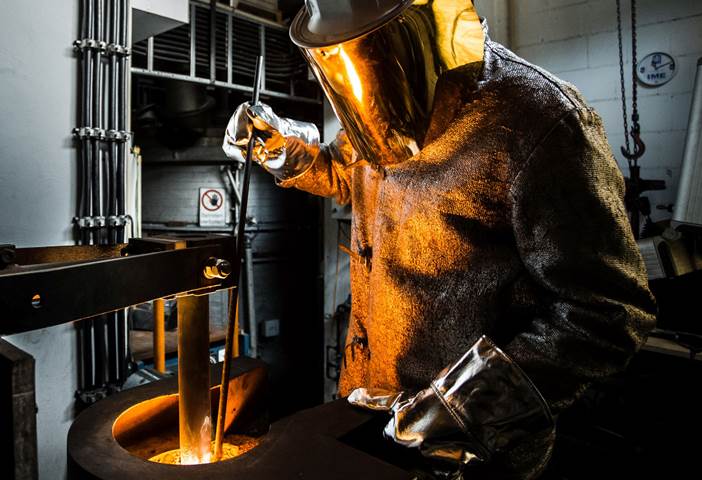
The primary production of metals is usually accompanied by by-product residues. These residue streams are a potential problem due to environmental concerns. Contained in these residues are valuable metals in lower grades than the primary production source. The IME is seeking means to exploit these vast secondary resources for value reclamation through development of innovative processes. The focus areas include and are not limited to the following: slag cleaning for recovery of precious metals, landfill mining to recover metals and plastics, red mud processing for recovery of high value metals such as Sc and Ga. Inertization of slags is another large research focus. Metallurgical slags can be modified so that they may be used e.g. as cement additives or as road building materials. This “zero-waste” approach contributes enormously to a sustainable metal production, which is actively propagated by IME in R&D projects and teaching.

Legierungmetallurgie
Aufgrund steigender Anforderungen an metallische High-Tech Werkstoffe hinsichtlich Zusammensetzung, Reinheitsgrad und Homogenität nimmt die Komplexität der Legierungsmetallurgie kontinuierlich zu. Den strengen Toleranzen wird mit dem Einsatz metallurgischer Vakuumprozesse begegnet, die beispielsweise das Schmelzen sauerstoffaffiner Elemente, die Entfernung gelöster Gase oder nichtmetallischer Einschlüsse sowie die selektive Destillation leicht flüchtiger Metalle ermöglichen. Prozesstechnisch stehen der Projektgruppe Legierungsmetallurgie dazu am IME diverse Vakuuminduktionsöfen, eine Druck-Elektroschlacke-Umschmelzanlage und ein Vakuumlichtbogenofen zur Verfügung. Aktuell werden unter anderem die folgenden Forschungsprojekte bearbeitet:
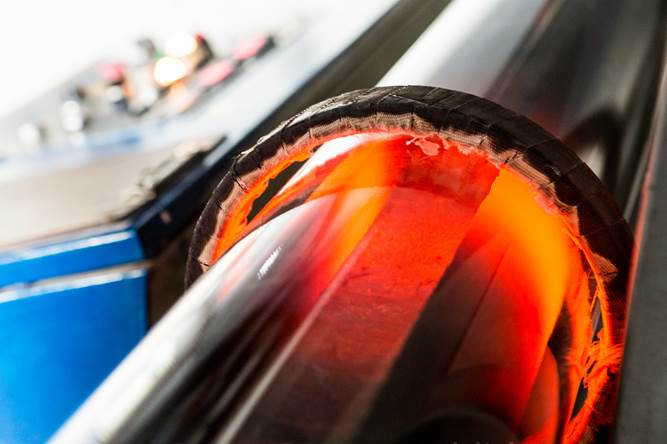

Pure Metals
The rapidly growing development and progress in the semiconductor, solar panel, photovoltaic and also the catalytic industry, has recently considerably increased the production and the number of applications of high-purity metals. In order to ensure the extremely low level of impurities (ppm or even ppb range), complex and highly controlled processes are required. The Pure Metals Group at IME focuses on alternative and cost-efficient methods, particularly based on the principle of fractional crystallization to produce high-purity metals such as Germanium, Indium, Antimony but also Aluminum, etc.
SeRoBatt - Sekundäre Quellen kritischer Rohstoffe für die Batteriezellfertigung – Potenziale, Rückge-winnung, Resynthese
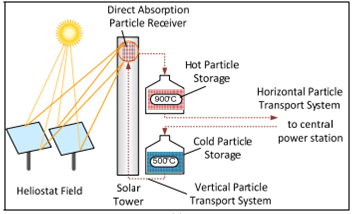
Solar
Kurzschlüsse - Entwicklung eines kleinskaligen Verarbeitungswegs für das lokalisierte Kurzschleifen-Recycling von Elektronikschaltplatinen

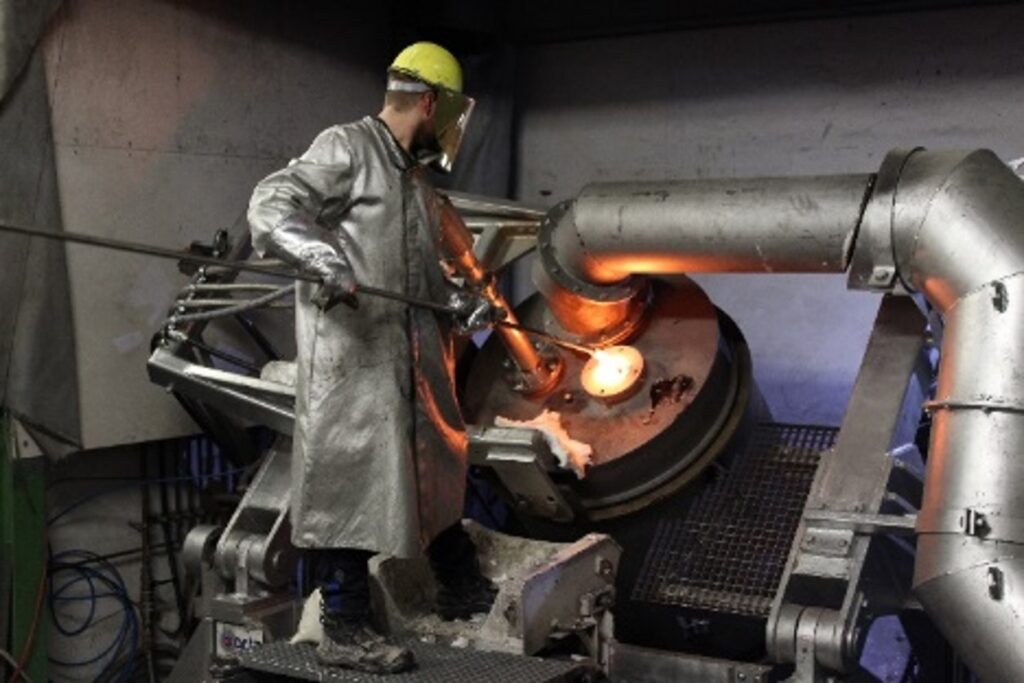
EURO-Titan: Rückgewinnung von dekarbonisiertem Titan aus Aluminium- und Titanproduktionsrückständen

HEEERO - Hydrometallurgische Elektro- und Elektronikschrott-Recycling Optimierung

EarLi: Extraktion und Aufreinigung von Lithiumhydroxid Monohydrat aus gebrauchten elektromobilen Li-Ion Batterien für die Batteriezellfertigung

International Masters Programme in Energies & Green Hydrogen(IMP-EGH)

MeteoR - Mechanisch-thermochemische Verfahrenskombination für das Recycling von Feinfraktionen aus Abfallbehandlungsanlagen

PHöMixBeton - Prozess zur Herstellung alkalisch-aktivierter Binder durch das Schmelzen mineralischer Reststoffe für ein ökologisch gesteuertes Mixdesign von Beton

HVBatCycle - HV-Batterie Recycling- und Resynthese-Prozesse für nachhaltige und funktionserhaltene Materialkreisläufe

CO2-freie Aluminiumherstellung

CLIMA - Chemikalienfreie Lithiumrückgewinnung aus Lithium-Ion basierten Altbatterien

Erstellung eines Gewinnungskonzeptes für Te-Metall durch Reduktion sowie dessen Reinigung bis zur Herstellung hochreines Te.

EarLi: Extraktion und Aufreinigung von Lithiumhydroxid Monohydrat aus gebrauchten elektromobilen Li-Ion Batterien für die Batteriezellfertigung

Bildung Ta-reicher Magnetitphasen in WEEE- Recycling-Schlacken durch Modifikation und kontrollierte Abkühlung
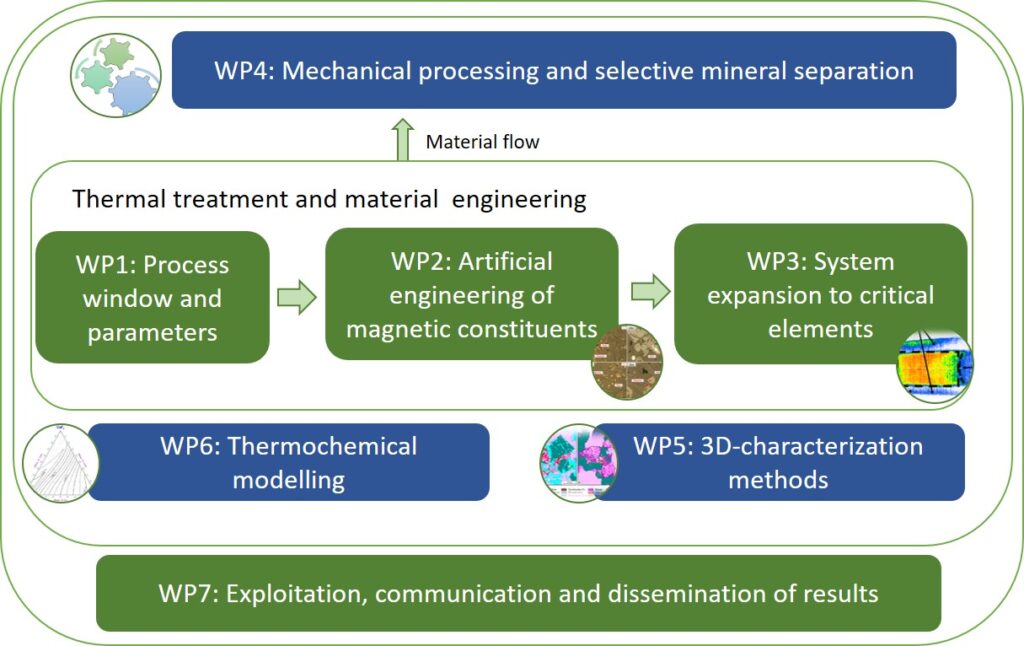
Zentrales Projekt - Schlackensynthese, Design und Charakterisierung

SMART - Anwendung von Künstlicher Intelligenz für Abwasserbehandlungsprozesse in den Ländern des Westbalkans

HARARE - Wasserstoff als Reduktionsmittel in der Metallurgie zur Rückgewinnung von Metallen aus metallurgischen Abfällen Projekt Art

SeRoBatt - Sekundäre Quellen kritischer Rohstoffe für die Batteriezellfertigung – Potenziale, Rückge-winnung, Resynthese

Solar

Kurzschlüsse - Entwicklung eines kleinskaligen Verarbeitungswegs für das lokalisierte Kurzschleifen-Recycling von Elektronikschaltplatinen

EURO-Titan: Rückgewinnung von dekarbonisiertem Titan aus Aluminium- und Titanproduktionsrückständen

HEEERO - Hydrometallurgische Elektro- und Elektronikschrott-Recycling Optimierung

EarLi: Extraktion und Aufreinigung von Lithiumhydroxid Monohydrat aus gebrauchten elektromobilen Li-Ion Batterien für die Batteriezellfertigung

International Masters Programme in Energies & Green Hydrogen(IMP-EGH)

MeteoR - Mechanisch-thermochemische Verfahrenskombination für das Recycling von Feinfraktionen aus Abfallbehandlungsanlagen

PHöMixBeton - Prozess zur Herstellung alkalisch-aktivierter Binder durch das Schmelzen mineralischer Reststoffe für ein ökologisch gesteuertes Mixdesign von Beton

HVBatCycle - HV-Batterie Recycling- und Resynthese-Prozesse für nachhaltige und funktionserhaltene Materialkreisläufe

CO2-freie Aluminiumherstellung

CLIMA - Chemikalienfreie Lithiumrückgewinnung aus Lithium-Ion basierten Altbatterien

Erstellung eines Gewinnungskonzeptes für Te-Metall durch Reduktion sowie dessen Reinigung bis zur Herstellung hochreines Te.

EarLi: Extraktion und Aufreinigung von Lithiumhydroxid Monohydrat aus gebrauchten elektromobilen Li-Ion Batterien für die Batteriezellfertigung

Bildung Ta-reicher Magnetitphasen in WEEE- Recycling-Schlacken durch Modifikation und kontrollierte Abkühlung

Zentrales Projekt - Schlackensynthese, Design und Charakterisierung

SMART - Anwendung von Künstlicher Intelligenz für Abwasserbehandlungsprozesse in den Ländern des Westbalkans

HARARE - Wasserstoff als Reduktionsmittel in der Metallurgie zur Rückgewinnung von Metallen aus metallurgischen Abfällen Projekt Art












