Research » Titanium Metallurgy
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
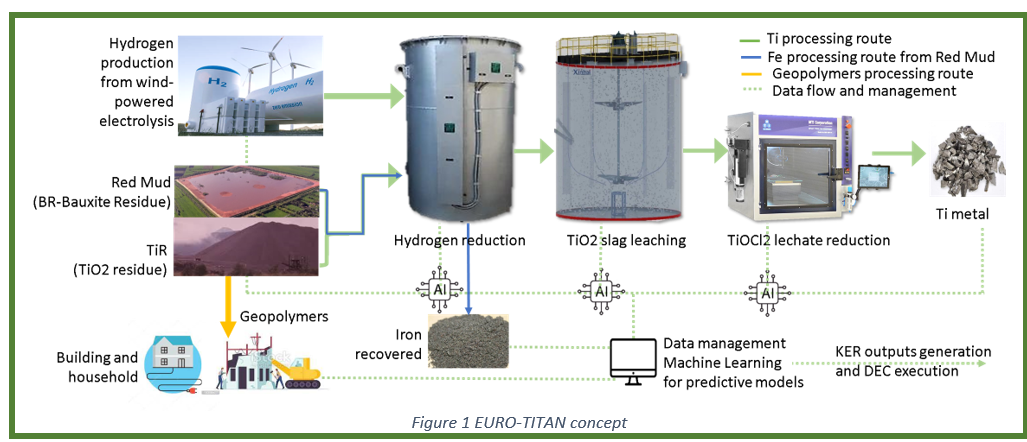
The main objective of EURO-TITAN is to provide traceable, continuous Ti- metal production through a disruptive low-C processing in and for Europe from mining and processing wastes to diversify the supply chain, while reusing residual material volumes, and reducing associated environmental risks and management costs. EURO-TITAN production will have the lowest C footprint (> 90 % reduction compared to the Kroll process) due to the utilization of 100 % raw material from waste streams with a full integration of hydrogen technologies and renewable energy sources. Hydrogen will be produced onsite with electrolysis and electricity from wind power in partnership with our Associate partner Salzgitter AG.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
The project presents an innovative approach to the sustainable use of titanium alloys and to significantly increase the material efficiency of the most commonly used alloy – TiAl6V4 – including the development of an optimized lightweight composite material for additive manufacturing, in the automotive and aerospace industries. The overall objective of this project is to produce a high-quality powder for additive manufacturing from industrial waste by an innovative and cost-effective process route and to meet the political demand for a circular economy strategy.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
In terms of content, the Skin Pro project is a continuation of the previous Skin project and focuses on the technological advancement of the manufacturing process of TiAl low pressure turbine blades to production maturity. This includes both the progression of the casting and forging process as well as the optimization of the component allowance along the entire production chain. Furthermore, the development of know-how in process control and material properties plays an important role. In addition, as part of the optimization of the melt recycling process for cycle material in the VIM casting process, it is necessary to develop tailored master alloys to compensate for melt losses. The overarching goal of technology development is the required verification of microstructural and property conformity along the process chain according to given specifications. Finally, a technol.-econom. consideration of potential production routes for the utilization of the mold technology takes place.

Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
The current synthesis of titanium and titanium alloys is extremely cost-intensive. This is due to the large number of process steps and the low space-time yield. The use of titanium and titanium alloys is essentially limited to special applications such as aerospace, submarine construction, weapons technology and medical technology. A potential field of application is the automotive industry to reduce mass and CO2 emissions. In addition, the corrosion resistance and reliability of engines could be significantly increased. Within the framework of the DFG research group FOR 1372, research was carried out on the motif of cost reduction in the production of titanium and titanium alloys with minimized process stages. The focus was on the direct use of natural TiO2 ore concentrates and the cost-effective production of synthetic TiO2 as a raw material for titanium alloys.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
The research and development of refractory components for titanium metallurgy based on CaZrO3 and their transfer into industrial practice in casting technology and for the production and recycling of titanium materials. This involves the intensive investigation of an adapted metallurgical process technology and the interaction at the interface between melt and refractories with the aim of melting low-contamination titanium materials in vacuum induction melting furnaces for mould casting, recycling and primary material recovery.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
In the last 5 years, an investment casting route has been successfully developed for the production of “near-net-shape” Low-pressure turbine blades made of TiAl for aviation. This production route is currently in the validation phase on the part of OEM´s, which means that the introduction of this technology in series production will become increasingly probable in the foreseeable future. The aim of the TiAl-2020 project is to improve the sustainability and economic efficiency of the production process by developing processes to recycle the valuable raw materials required for the process. These include TiAl scrap and ceramic residues, in particular Yttrium oxide, which previously had to be disposed of as waste products and could not be reused sensibly.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Research Area
Description
Titanium alloys are industrially produced by melt metallurgy, with repeated remelting to achieve the required quality. Further process steps are needed to adapt the microstructure to the requirements, which is particularly important in aerospace applications. By molten salt electrolytic deposition, it would be possible to produce titanium alloys in a few process steps. By varying the deposition parameters, the microstructure can be adjusted.
There are possibilities in the field of surface technology and electroforming, up to the direct production of slabs and sheets, as well as the production of powders for powder metallurgical processes.
As an application example of the technology to be developed, the production of titanium matrix composite materials is planned. Here, silicon carbide fibers are coated with the titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V and then compacted into a composite material.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Research Area
Description
Future aero engines will need to be more efficient and contribute to the reduction on environmental impact of air transportation. They must reach some standards of performance by reducing emissions and creating some savings on operation costs. EIMG consortium has launched since several years some initiatives to develop future engines in the frame of the European Committee research programmes. Within different project such as DREAM, VITAL, NEWAC or LEMCOTEC, EIMG is ensuring the development of innovative technologies in order to further reduce the fuel burn, emissions and noise. In order to ensure the technological breakthrough, future aero-engines will have higher overall pressure ratios (OPR) to increase thermal efficiency and will have higher bypass ratios (BPR) to increase propulsive efficiency. These lead to smaller and hotter high pressure cores.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
This project is dedicated to develop all processing aspects necessary to qualify intermetallic materials for technical applications. During processing of titanium aluminides by casting routes, 90-95% of the total input material is converted to scrap of different qualities. It is thus of strong relevance for a sustainable development of technical TiAl-alloys to prove and establish an integrated recycling process, enabling the reuse of an energy-intensive and costly material within the required specifications.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
This subproject is part of the development of a process step minimized process for the production of titanium and titanium alloys. It comprises basic investigations and associated modelling in the field of solid aluminothermics and the development of an innovative electroslag remelting process with maximized refining potential.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
Gamma Titanium aluminides are high-performance materials that are produced through a complex process chain, resulting in considerable production costs. With an alternative recovery process in which titanium oxide is reduced to metal together with aluminum and oxides of other alloying elements in an aluminothermic reaction, titanium aluminides can be cost-effectively generated directly from the oxidic starting materials by subsequent deoxidation with an active CaF 2 slag. In addition, the IME is designing a process for recovering the considerable amount of scrap produced by the conventional process route. The aim of the project is to quantitatively examine the influence of the accompanying elements calcium and fluorine on the oxidation behavior and the mechanical properties of titanium aluminides, which are unavoidable in this novel production process and the recycling process, and to discuss their respective mechanisms of action. While the mode of action of calcium in titanium aluminides has been almost completely unexplored to date, fluorine is known to have a very favourable effect on oxidation resistance when enriched in the near-surface area. For the first time, fluorine as an alloying element in the TiAl volume material is to be investigated in the proposed project and a process window for titanium aluminide production determined, in which calcium and fluorine ideally have a positive effect on the mechanical properties and oxidation behaviour of titanium aluminides. Important scientific findings with considerable application relevance for this modern class of materials are expected.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
A concept for the recycle of low-grade titanium scrap for reuse in a low-cost titanium alloy is being investigated. The process consists of the stages of material conditioning, vacuum induction melting (VIM) and electroslag remelting (ESR) as well as a remelting step in the vacuum arc furnace (VAR) for materials with the highest purity requirements. The metallurgical investigations can prove that technical contamination of titanium alloys from the supplied scrap can be tolerated for non-flying applications of corresponding alloys of up to two percent and may even lead to significant property improvements, in particular the strength properties. The task of the IME work package is to investigate the influence of the contamination level of titanium recyclate alloys.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
Starting from a titanium ingot weighing 1.8 t, which is formed during the constituent melting of titanium sponge and is the starting material for about 1 t of titanium semi-finished product, a maximum of 0.4 t of end product can normally be produced due to the complex geometries of typical titanium components. In special cases, even more than 90 % of the semi-finished product is machined, so that a component mass of just 100 kg is achieved. The scrap resulting from the casting process (webs, casting funnels, wax channels, melt residues, etc.) may not only be contaminated with moulding materials, but also show deviations in composition due to segregation effects.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
The overall objective of this research project is to extend the understanding of the Ar-ESU process through mathematical modelling and simulation as well as the experimental investigation of impulse, heat and mass transport in the ESU process. To describe the melting behaviour of the electrode, the interaction between metal and slag and the solidification process, a model is formed which is solved numerically with the commercial CFD program FLUENT. This model enables detailed knowledge of the flow behaviour of the salt slag and the titanium melt with additional consideration of external effects, such as the inductive stirring effect through the power supply lines. Among other things, it allows statements to be made as to whether non-metallic inclusions are absorbed by the slag without settling again in the metal bath, how long the average residence time of the metal droplets in the slag bath is, and under which conditions optimum, i.e. uniform melting behaviour of the electrode across the cross-section, can be achieved. These statements can be used, among other things, for the optimization of current process controls in ESU systems. As an example, the refining of titanium scrap under argon shielding gas is to be investigated, since in this process, in addition to the physical effects within the electrode-slag-metal bath system, chemical reactions take place between metal and slag, which cause additional effects.
Title
Type
Sponsorship
Duration
Partner
Research Area
Description
The main goal is to achieve a cost saving potential by shortening the process chain and by using cheaper mass raw materials. From a scientific-technical point of view, the project represents the development and testing of a process with the aid of published laboratory results for various individual process steps. The proposed process for the cost-effective production of Ti-Al (X) alloys (X = alloying addition, e.g. niobium) or y-titanium aluminides. The development will first be carried out on a laboratory scale, the further development on a pilot plant scale. The starting material will be rutile or preferably the low-cost TiO2 white pigment available in appropriate purity and in large quantities (annual production > 1,000,000 t).


